Built on a modular system called ModuRail, these devices are usually accompanied by NR5 power output modules and/or passenger information system modules and distributed control modules with communication via CAN.
Master control is implemented via a CRV_AVV module which collaborates with the vehicle control computer and expands its functions.
Control computers are complemented by engine driver displays, ARR or ARR_AVV keypads and information point sensors.
ModuRail – 19“ Modular System for Vehicle Control Computers
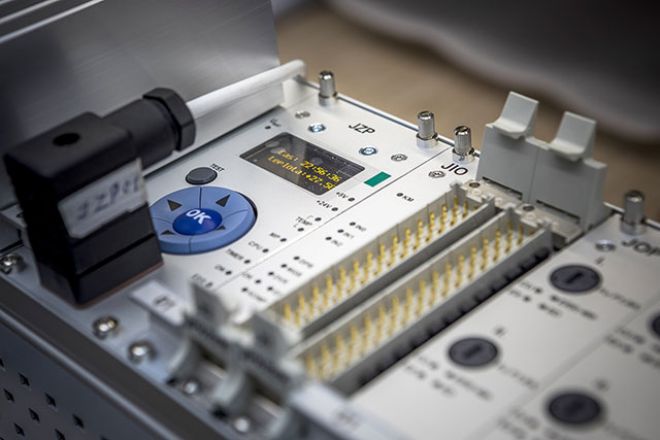

ModuRail is a modular microprocessor system that uses 16- and 32-bit Fujitsu processors. It is designed primarily for building rail vehicle computers which provide the following functions in particular:
- controlling driving modes and train control devices
- controlling the excitation of the alternator of the main and auxiliary drives
- automatic speed regulation along with control of the coaction of various types of brakes via anti-slip and anti-skid regulation
- vehicle-to-vehicle communication and multiple-unit control of traction vehicles of any traction
- automatic train operation
- reading, displaying and recording operating data and faults, vehicle diagnostics
- linking to protection equipment
- measuring, displaying and registering train speed and other information
MSV elektronika's control and diagnostic computers implement multiple-unit vehicle control via standardised WTB or national train buses.
CRV_AVV Master Control Module
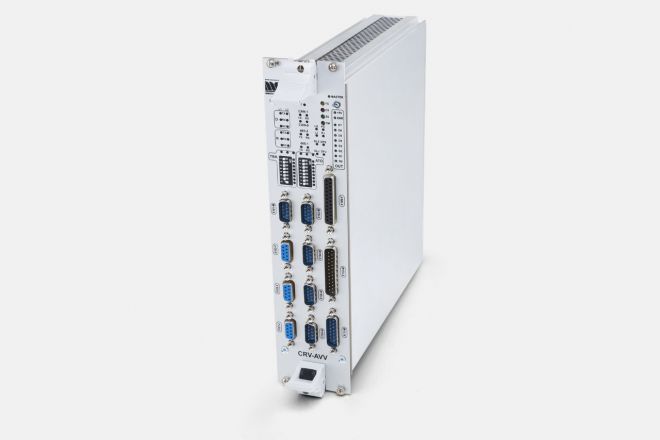

The master control module allows for the operating of traction vehicles at various levels of automation. It allows for the multiple-unit control of locomotives or controlling the locomotive from the control car, and supports the coaction of pneumatic and electrodynamic braking systems in all modes of automation.
The module collaborates with the vehicle's control computer, which responds to the commands from the master module to control the traction group of the locomotive and its auxiliary drives in particular.
The main standard controllers for the CRV_AVV master control module are the main thrust lever, train driver keypad, driving mode selector, driving direction selector and auxiliary function controller of the DAKO brake valve. Train position is read by MSIB magnetic information point sensors.
The module allows controlling the vehicle (train) in four modes: MAN – manual, AUT – automated, CB – automated with braking to destination, OJV – automated with braking to destination and drive optimisation.
Specification Sheets
Colour Screens
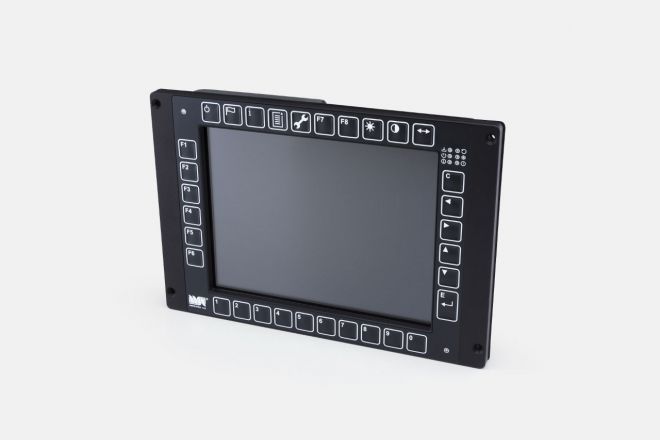

Colour screens developed and produced by MSV elektronika are designed primarily for use in rail vehicles, but can also find application in industrial environments.
The screens are fitted with a TFT display and membrane keys along their perimeter. Brightness regulation ensures legibility of the displayed information even under the variable light conditions in the cab.
The interior and display surface of the screen is heated and features temperature regulation to ensure problem-free operation and initialisation even at low temperatures.
By default, the screens come fitted with three galvanically separated CAN lines, a USB service line and Ethernet.
BKL Train Driver Keypad
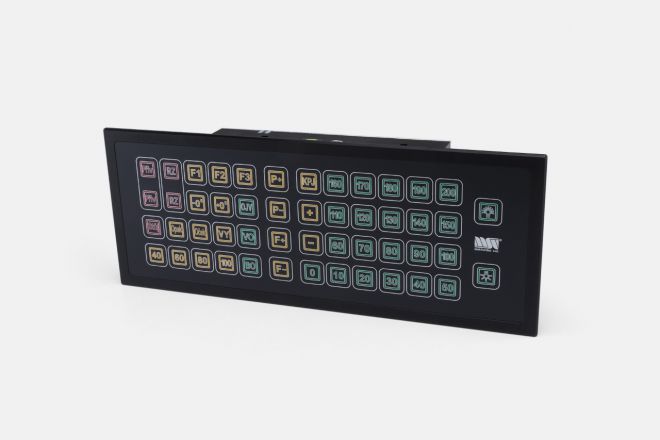

The keypad is a micro-processor device for communication between the operator and the control system.
It allows the train driver to input commands in driving modes with automated speed regulation (ARR), or automated train operation (ARR_AVV). The number and arrangement of keys on the keypad differs based the purpose of the keypad.
The keypad buttons are backlit and their brightness can be adjusted by the driver. The symbols on the buttons are interchangeable and can be modified during production as needed.
The keypad communicates with the master control device in the vehicle through a CAN serial line, optionally also with CAN OPEN protocol.
Magnetic Information Point Sensors
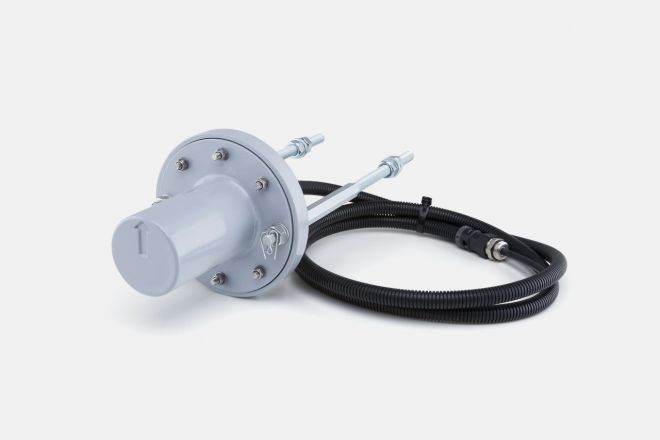

Magnetic information point sensors are a standard peripheral to the CRV_AVV system. They are used for detecting where the traction vehicle or the control car fitted with information points is located on the track.
MSIB magnetic information point sensors make use of the vehicle control computer's hardware and software to read the AC dual-polarity magnetic fields of a track information point, which is a stationary portion of the automatic train operation (AVV) subsystem. The electronics of the sensors are designed in a way that allows the on-board computer to determine the proper functioning of the sensors.
CAN Distributed Control and Data Collection Units
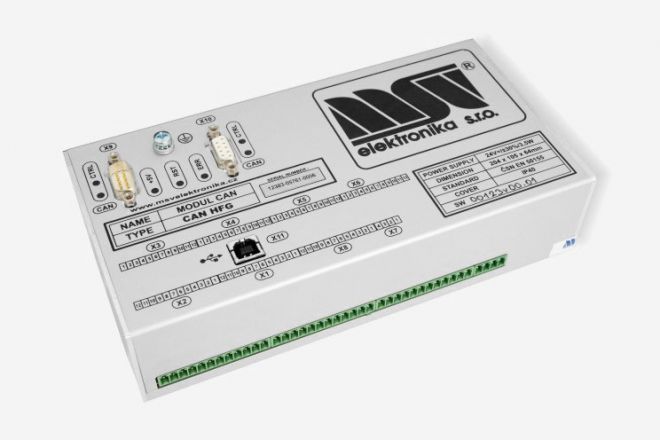

CAN units are electronic modules designed primarily for distributed data collection, control and management of processes in vehicles and in various industrial applications. The modules are produced in several input and output configurations.
Each module contains two CAN communication lines and a USB line. The modules may also come with an 2x16 character illuminated alphanumerical display and membrane keys (arrows for navigation in the menu) or without these display features.
The USB line is used for diagnostics, testing and uploading of operating software and uploading and reading EEPROM memory. CAN lines can be used to connect modules into a hierarchical network.
The CAN module features 24 slots that can be variably fitted with input and output modules with various parameters to the customer's specifications.
Gateway Train Bus Adapter
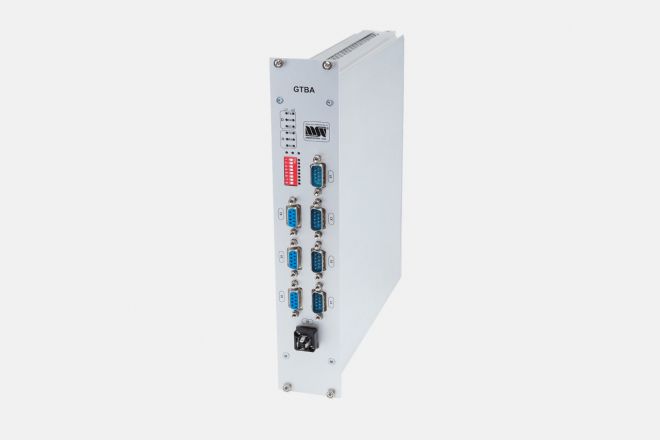

The GTBA plug-in unit is used for vehicle-to-vehicle communication for all propelled and propelling rail vehicles of all tractions via the ČD NVL national train bus, primarily through a UIC cable. Its use for the NVL standard is similar to the WTB gateway, giving manufacturers of vehicle control systems an easy way to handle vehicle-to-vehicle communication. The vehicle's control systems are usually connected to the GTBA unit through an RS485 (2x) or CAN bus (2x) serial interface
The GTBA unit is designed as a plug-in unit for installation into a 19“, 6U tall cabinet, but can also be mounted separately.
MCR Wireless Communication Module
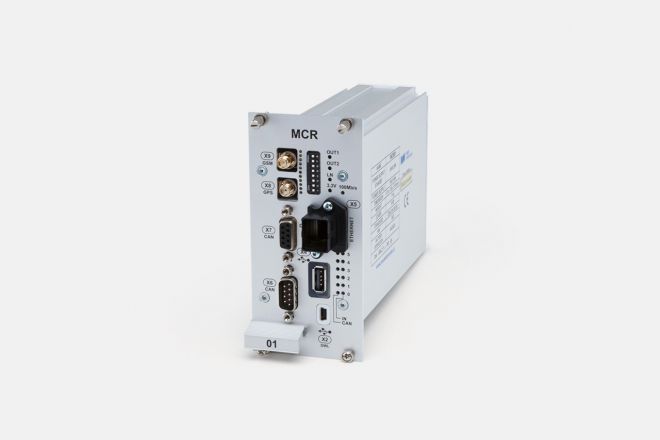

The MCR wireless communication module consists of two parts:
- The mobile unit of the MCR system
- The server unit of the MCR system
The mobile unit of the MCR system is located in the locomotive's cabinet rack cabinet and is linked via communication lines to the vehicle's other systems (diagnostic computer, central regulator of the vehicle, tachograph etc.). The unit also allows for the determining of the precise location of the vehicle through a GPS module.
The main purpose of the unit is to collect diagnostic data from connected systems and send this data through a GSM network to the MCR server application. Return communication from the server application is also possible. The mobile unit is capable of receiving data and commands from the server application and performing the commanded actions (e.g. displaying received data on the screen).
The server application receives and stores data from all MCR units into its own database. The data is then accessible to all users after login. The database allows for the viewing of diagnostic information about all owned vehicles.
Functions of the MCR system
- collecting diagnostic data
- determining the position of the vehicle
- identification of the train driver
- determining the condition of the locomotive
- determining fuel level
- sending regular vehicle condition reports
- alerting about assaults on the vehicle
- transmitting the position of the vehicle
- backing up collected data and making it accessible to users
